Causes and risk factors of atrial fibrillation
The disease occurs mainly in older age or in younger patients with risk factors. However, those affected often include older, well-trained endurance athletes.
Do you have a finding and would like a second opinion or are you not sure whether you have atrial fibrillation? One of our specialists will be happy to take the time for a consultation.
There are numerous causes for this - and it can not infrequently be due to the respective lifestyle. Most often, symptoms such as dizziness, loss of consciousness, shortness of breath or chest pain lead to the diagnosis. And a stroke can also be the first sign of the presence of this cardiac arrhythmia. In most cases, however, the presence of atrial fibrillation is discovered by chance - for example, during a preliminary examination or a (cardiological) check-up.
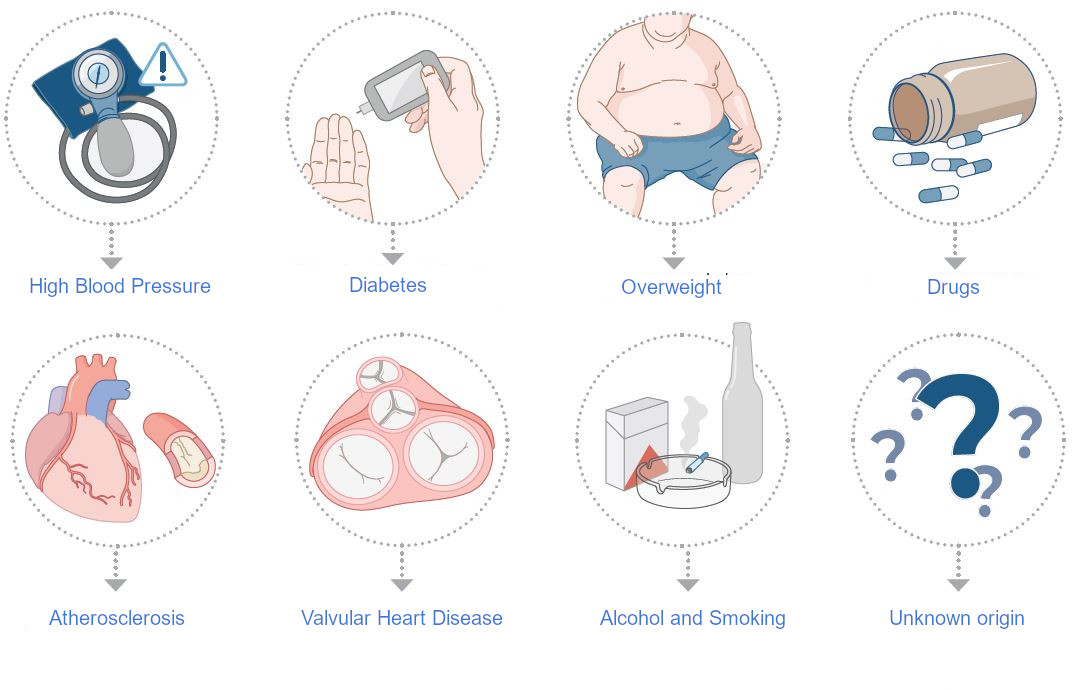
Common Causes
Age, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, alcohol consumption, drug abuse, hyperthyroidism, sequelae of heart failure, coronary artery disease, valvular heart disease, postoperative sequelae, endurance sports, pericardial diseases asthma, COPD or sleep apnea syndrome.
When is it atrial fibrillation?
The healthy heart rhythm is regular, unconscious, but also variable and perceptible as a pulse wave that passes through the body. Normally, the beat of the human heart emanates as an electrical impulse from the sinus node in the right atrium and adapts very quickly to the respective physical, emotional and psychological stress. In this (normal) situation, the heart is thus in sinus rhythm. In atrial fibrillation, this rhythm is disturbed and the heart consequently no longer beats regularly, also perceived as heart flutter.
Usual symptoms
As a rule, the symptoms vary greatly. There are patients who experience no symptoms at all, i.e. do not notice the atrial fibrillation themselves and only receive the diagnosis through a complication, such as a stroke. Other people, on the other hand, notice atrial fibrillation clearly. This may be due to an inappropriate pulse rate, reduced cardiac output or other symptoms of the disease. However, there are also patients who experience severe shortness of breath or even panic attacks at the slightest sign of atrial fibrillation.
Common symptoms of AFib
- Irregular heart beat
- Heart pounding
- Heart racing
- Palpitations (= the subjective feeling that the heart beats too fast and too strongly or irregularly)
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Difficulties breathing
- Inner stress
- Fear, Panik
- Exhaustion
- Tiredness, Lack of endurance, ...
- Chest pain
- Stroke
Is atrial fibrillation (afib) dangerous?
If atrial fibrillation is treated correctly and in time, it does not pose an acute danger to the patient. This is because, as already mentioned, those affected can either suffer from severe symptoms that can significantly reduce their quality of life - or not notice any of them. It is important to know, however, that atrial fibrillation increases your risk of suffering a stroke or cerebral apoplexy fivefold. As a result of the irregular heart activity, blood clots can form in the left ear of the heart and spread throughout the body, clogging smaller vessels. In the brain, this can then lead to the previously mentioned stroke.
The so-called CHA2DS2-VASC score for patients with atrial fibrillation is now available - this allows the risk of thromboembolism in a patient with atrial fibrillation to be assessed on the basis of risk factors in the patient's medical history. This is then used to derive an appropriate treatment recommendation with a blood thinner. For patients who have AF but score 0 on the CHA2DS2 VASc score, no therapy is recommended. For all others - more is better than less! A cerebral stroke can have devastating consequences. Accordingly, blood thinning is absolutely necessary. For selected patients, who cannot take a blood thinner for various reasons the so-called heart-ear occlusion is an alternative worth mentioning. However, a prolonged, irregular and too fast heartbeat may over time lead to the development of cardiac insufficiency (heart failure). Therefore, untreated atrial fibrillation can lead to increased mortality, hospitalization and / or a significant impairment of your quality of life.
Origin of AFib
Atrial fibrillation originates in the pulmonary veins. At the point where the pulmonary veins enter the left atrium of the heart, a kind of "misfiring" occurs. This throws the whole atrium into electrical chaos - atrial fibrillation. The heart rhythm is disturbed and no longer regularly transmitted to the large heart chambers (the ventricles). The cornerstone of atrial fibrillation therapy is therefore pulmonary vein isolation (PVI). This isolation can be created by scarring the veins, which prevents the triggers of atrial fibrillation from throwing the heart into this chaos. Ablation is then performed for this purpose - either from the inside, using a catheter, or surgically from the outside.
Classification of AFib
Atrial fibrillation can be a one-off or more frequent event and also varies from patient to patient. Depending on the occurrence, duration and reversibility (= healing without permanent damage or impairment), atrial fibrillation (abbreviated: AF) is considered to be seizure-like (paroxysmal), persistent (persistent) or permanent (permanent):
- Paroxysmal AFib (cryoablation as initial therapy). Also called intermittent atrial fibrillation, it occurs spontaneously and seizure-like, but usually disappears on its own within 24 hours. This is why this form of atrial fibrillation is called "self-limiting". Patients usually have a normal sinus rhythm and the atrial fibrillation occurs only sporadically. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation most commonly occurs in the left atrium around the pulmonary veins and can be treated by electrically isolating the pulmonary veins from the atrium so that the pulmonary veins can no longer interfere with the electrical transmission in the atrium. A number of so-called "triggers" are now known to trigger paroxysmal atrial fibrillation; these include alcohol (especially excessive drinking), obesity, caffeine (especially in the form of a ristretto or energy drink), recreational drugs and smoking. If these triggers are avoided, atrial fibrillation also decreases.
- Perisistent AFib. Persistent atrial fibrillation usually lasts for more than seven days or can only be corrected by medical means (by taking medication or with the help of electric shocks (= cardioversion)). Persistent atrial fibrillation is more complex in its development and does not usually return to sinus rhythm on its own. However, thanks to cardioversion, it can be brought back into sinus rhythm. Persistent atrial fibrillation originates in the left atrium and is transmitted to both atria with increasing fibrosis (proliferation of connective tissue fibres in an organ).
- Permanent AFib. Permanent (enduring) atrial fibrillation is accepted by patients and doctors alike, and cessation by medical means is no longer sought. If necessary, the symptoms are treated and possible consequences are prevented. However, in the case of permanent atrial fibrillation with a sustained pulse of over 100 beats per minute, this must be slowed down. If the medication is not sufficient or is not tolerated by the patient, the implantation of a pacemaker can be considered. It is also important to avoid possible further complications by using a blood thinner.
How do we diagnose atrial fibrillation?
In order to be able to determine the presence of atrial fibrillation, we doctors first question the person affected with regard to their complaints and symptoms. This is followed by further diagnostic procedures. Finally, atrial fibrillation can be diagnosed using an electrocardiogram (ECG) or a long-term ECG. And - as already mentioned - smartphones or an Apple Watch are now also suitable for indicating atrial fibrillation.
If the atrial fibrillation only occurs occasionally, it becomes difficult to record it taking into account a snapshot (= the ECG). That is why long-term ECGs are carried out in such cases. However, there are more reliable methods that allow continuous ECG recording. The way these devices work varies (they can be stuck on with a plaster or placed under the skin).
Once the diagnosis has been made, all possible causes for the presence of this arrhythmia must be ruled out. To do this, we cardiologists perform an echocardiogram (a heart ultrasound) and an exercise ECG and take blood from the patient. In addition, a CT (computer tomography) may be ordered or the insertion of a heart catheter may be necessary.
Typical ECG reading of a healthy heart
The heart current curve is made up of various waves and spikes that make the course of the electrical impulses in the heart visible.
Here is the ECG curve of a healthy heart - the sinus rhythm. The large spikes (= the QRS complexes) follow each other very regularly. The smaller elevations in front of these spikes (represent the so-called P-waves), testify to good sinus node activity. This is sinus rhythm.
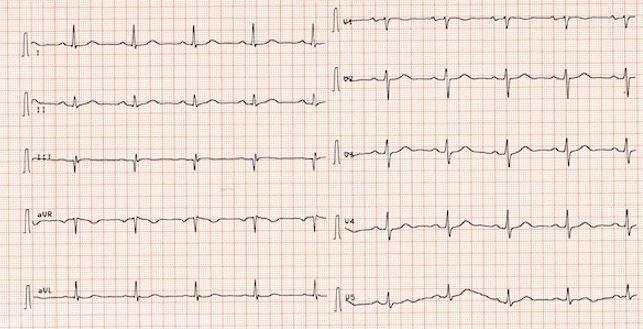
ECG in atrial fibrillation
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is performed to confirm the "atrial fibrillation" diagnosis. The following ECG shows an absolute arrhythmia. The large spikes (= the QRS complexes) as well as the baselines are - recognisably - completely irregular. Smaller elevations in front of these deflections, on the other hand, no longer exist. In paroxysmal atrail fibrillation the phases of fast atrial fibrillation can change back and forth with sinus rhythm.

Increased quality of life thanks to state-of-the-art treatments
Our therapy methods in connection with AFib aim to significantly improve the impairment of your quality of life again, to reduce your symptoms and noticeably minimise the risks of untreated atrial fibrillation, to prevent heart failure and cerebral stroke and to proactively avoid associated late effects.
Our methods also allow you to quickly stop taking your medication and, most importantly, to stop taking your blood thinner after surgery. In the following section you can learn more about the therapies we offer.
Specialized on complex AFib
Our innovative centre specialises in the diagnosis and treatment of atrial fibrillation - especially persistent or complex atrial fibrillation, which can occur in previously treated patients after one or more catheter ablations.
We - that is Prof. Salzberg, MD, and Dr. van Boven - introduced surgical ablation at the University Hospital in Zurich more than ten years ago. Since then, we have successfully treated numerous atrial fibrillation patients with this method. Take a look at our patient videos with Prof. Dr. med. Salzberg and learn more about his results in connection with the performance of surgical ablations for atrial fibrillation.
As is usual in modern cardiac medicine, an interdisciplinary team of cardiologists and cardiac surgeons also plays the leading role in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. Incidentally, this way of working is also prescribed in this form by the current guidelines of the major professional societies.
Recommended course of action
If you feel you may be suffering from atrial fibrillation, we strongly recommend an examination by your family doctor or a cardiologist of your choice. In the first step, the causes of the atrial fibrillation must have been clarified and a first attempt at therapy should already have taken place. If you are already at this stage and need further support, then you are welcome to make an appointment with our team at any time.