Palpitations
The most common tachycardias
The normal resting pulse rate is between 60 and 100 per minute. It is individually very variable and is influenced by various factors (gender, age, fitness level, body weight, medication, etc.). The heart constantly pumps oxygen-enriched blood through the body like an incessantly running motor. Under stress, the heart rate should increase - if this does not happen, we speak of chronotropic incompetence. This is usually the result of a disease or age-related degeneration of the heart's main clock generator - the so-called sinus node. If the inadequate heart rate increase or sinus bradycardia leads to symptoms such as dizziness or even fainting spells, the implantation of a pacemaker can help.
We speak of tachycardia when the pulse rate rises to over 100 per minute at rest. Heart rates of more than 120 per minute are often perceived by many patients as "palpitations". This is to be distinguished from increases in heart rate that occur during physical or mental stress, but also in combination with fever, and which represent a completely normal physiological adaptation reaction in order to meet the body's increased oxygen demand due to the situation.
Tachycardia can originate in the main chambers of the heart, the so-called ventricles, or in the atria. In the first case, especially with pre-existing heart disease, it is often a serious situation that should definitely be clarified by a specialist. Tachycardia originating in the atria, on the other hand, is much less likely to lead to acute emergency situations. But here, too, you should at best have a clarification of the type and cause of the cardiac arrhythmia organised immediately after the first occurrence.
Do you have a finding and would like a second opinion or are you not sure if you suffer from tachycardia? One of our specialists will be happy to take the time in a consultation.
Tachycardia from the atria
Tachycardias from the atria
Sinus tachycardia
Accelerations in the activity of the heart's main clock generator - the sinus node - can usually be attributed to the body's own adaptation reactions (for example, in connection with exertion or stress) or to non-cardiac conditions such as oxygen deficiency, hyperthyroidism, blood loss or similar. However, if there is a noticeable, rapid increase in sinus rhythm even during low physical activity or during a period of rest, then inadequate sinus tachycardia may be present. In this case, it is not uncommon for there to be a change in the balance of the autonomic nervous system and not a cardiac arrhythmia in the true sense. Medication can help here (at least temporarily), but we have also had good experience with specific endurance training tailored to the individual patient.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia
This form of atrial arrhythmia is caused by increased automaticity of one or sometimes several muscle cell groups. This persistent cardiac arrhythmia can often only be insufficiently regulated with medication. For this reason, catheter ablation with targeted obliteration of the causative atrium is usually the treatment of choice.
In atrial flutter, electrical circular excitations occur in the atria - usually around the tricuspid valve, which is located between the right atrium and the right main chamber (so-called typical atrial flutter). The pulse is regular and rapid, the heart rate is usually around 150 per minute on average. Occasionally, cardioversion is necessary in such cases, but even in such cases catheter ablation has very good results and is relatively easy to perform.
Atrial fibrillation
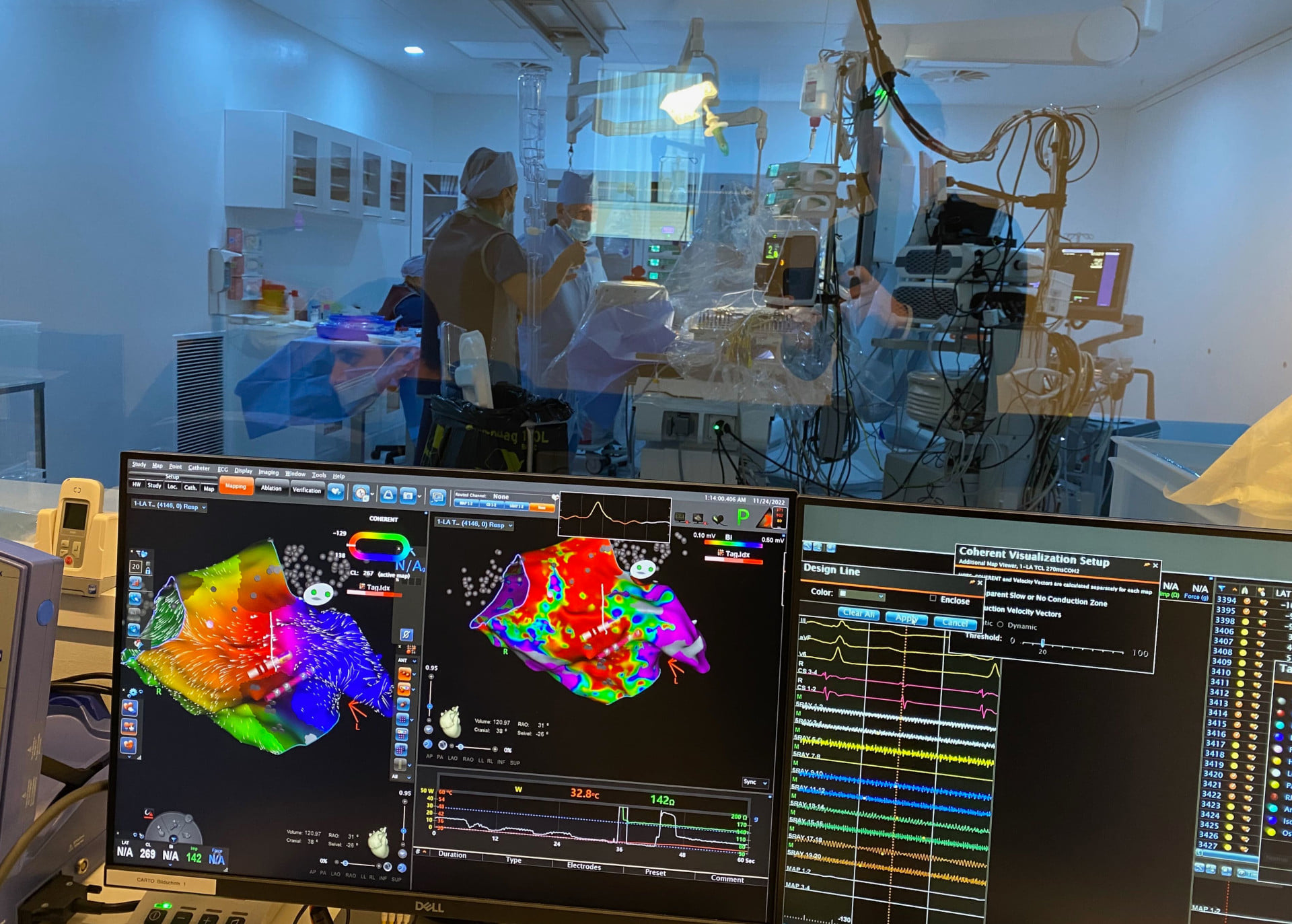
By this the cardiologist means an absolute arrhythmia. In this case, there is a chaotic spread of excitation with travelling fibrillation waves in both atria of the heart. The cause is often age-related changes in the fine architecture of the musculature - especially of the left atrium. Statistically, the probability of developing atrial fibrillation increases from around the age of 50. Atrial fibrillation is almost always triggered by extra beats or volleys of extra beats from the sections of the pulmonary veins near the heart. These four blood vessels, whose main function is to transport oxygen-enriched blood from the lungs to the heart, can be electrically isolated by a special ablation technique (pulmonary vein or pulmonary vein isolation = PVI), which means that atrial fibrillation can no longer be triggered. These techniques can be catheter ablation on the one hand and surgical ablation on the other. Hybrid ablation is when these two techniques are combined.
Atrioventricular tachycardia
Atrioventricular tachycardias are tachycardias that can occur in patients with a congenital, special, electrical-anatomical variant of the conduction of excitation from the atrium to the main chambers. These include the "AV accounts re-entry tachycardias" and the "Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome". The treatment of choice in these cases is also catheter ablation, in which the additional conduction pathways can be gently obliterated with few complications.
Ventricular tachycardia
In all forms of palpitations or extra beats from the large ventricle, clarification of the underlying heart disease is absolutely necessary. Please never underestimate this, but pay attention to your heart health at all times!
Ventricular extrasystoles (also called Premature ventricular contractions (PVC)) are extra beats from the muscles of the main chambers. Most of the time they are benign, but they can lead to symptoms or anxiety and should therefore be medically clarified and controlled in the further course. The frequent occurrence (more than 10% of the total beats of the heart), extra beats from certain regions (for example from the Purkinje fibres) or the association with a serious heart disease are problematic. It is therefore important that in such cases the following can always be ruled out by a doctor: Circulatory disorder of the heart muscle, thickening of the heart muscle, heart valve defect, heart muscle disease and / or heart pump weakness.
Common causes of ventricular tachycardia are scarring of the main chambers after a heart attack and after severe vascular damage.
A defibrillator offers the best protection against these malignant tachycardias.
Other ventricular tachycardias are found in the rare, genetic rhythmological disorders such as long-QT syndrome, short-QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome and catecholamine-dependent polymorphic ventricular tachycardia.